

Canadian C-Spine rules are recommended due to their high sensitivity. Patients history and clinical examination is documented by using a structured protocol, neurological deficits have to be documented using the scoresheets of the American Spinal Cord Injury Association (ASIA, ). The Spine Section of the German Society for Orthopaedics and Trauma (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie, DGOU) has set up a working group to analyze strategies in German trauma and spine centers and is going to publish recommendations on the treatment of odontoid fractures. The optimal treatment remains controversial as there are many contributing factors. Despite numerous published articles over the past 2 decades. 3 In younger patients, the potential loss of C1/2 motion should be taken into account, thus anterior direct osteosynthesis or temporary posterior stabilization using Harms technique are better options in this patient group. 5, 6 In a recently published meta-analysis, posterior C1/2 fusion resulted in significantly higher fusion rates in the elderly. 1, 4 However, even operation results in nonunion rates of up to 33%. 3 Initially strong indications with fracture displacement >5 mm, angulation >10°, and the presence of neurological deficits are widened also considering the potentially high morbidity, instability and secondary displacement in conservatively treated patients. Management options for odontoid fractures have expanded with advantages in imaging and surgical technologies, with a trend toward primary operative stabilization. Injury treatment aims to reestablish stability of the atlanto-axial complex. 2 This fracture type is potentially serious due to the proximity of the medulla oblongata and the great mobility of the cranial-cervical junction resulting in a high risk of life-threatening neurological lesions. 1 In the elderly population, this fracture type represents the most common cervical spine fracture and in the population older than 80 years, the most common spine fracture of all. Odontoid fractures are widely common and reported to account for up to 15% of all cervical spine injuries. As there is still some bias in the treatment algorithms, the working group recommends establishment of a prospective study to result in more objective statements. In the aged population (>80 years), operative therapy is critical as postoperative morbidity complication and mortality rates rise significantly. In these cases, posterior instrumentation or fusion of C1 and C2 is favorable. The technique is demanding and leads to elevated complication and failure rates if modifiers are apparent. Unstable and/or dislocated displaced odontoid fractures are treated by anterior osteosynthesis with 1 or 2 screws.
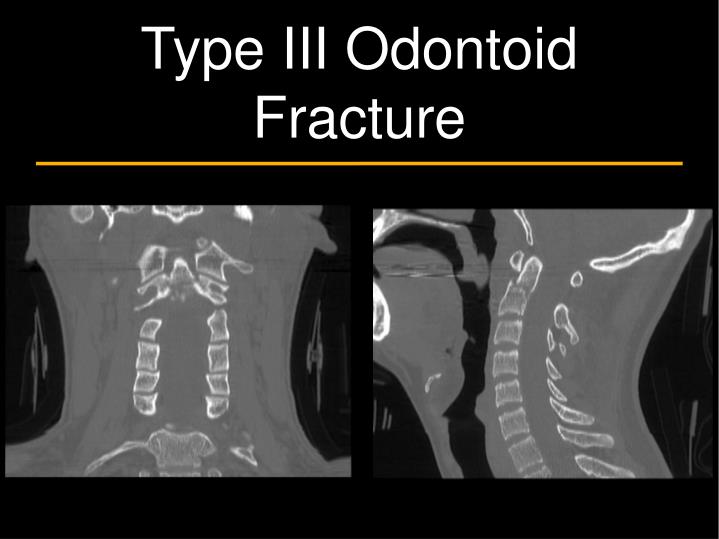
Stable odontoid fractures are treated conservatively non-operatively, but if so regular controls have to be performed. To create an adequate treatment algorithm, dislocation displacement and instability have to be identified. The classification of Anderson and D’Alonzo is still standard. If operation is indicated, many influencing factors have to be considered for appropriate approach and technique. Conservative treatment may also be started within stable nondislocated fractures, but then regular controls have to be performed. However, in the aged population, conservative treatment should be considered as morbidity and mortality rise significantly in the group of >75 years. Provider unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.Operation seems to be standard treatment for odontoid fractures. POA Indicators on CMS form 4010A are as follows: Indicatorĭiagnosis was present at time of inpatient admissionĭiagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admissionĭocumentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.Ĭlinically undetermined. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
ICD 10 ODONTOID FRACTURE CODE
Z87.311 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of personal history of (healed) other pathological fracture. This "Present On Admission" (POA) indicator is recorded on CMS form 4010A. POA Exempt Code The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
